|
PHOSPHOROUS PENTOXIDE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 1314-56-3 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 215-236-1 | |
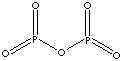
| FORMULA | P4O10 | |
| MOL WT. | 283.89 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
280920 | |
|
TOXICITY |
||
|
SYNONYMS |
Phosphoric Anhydride; Diphosphorus Pentoxide; | |
| Phosphorus Pentoxide; Phosphoric Pentoxide; Diphosphorus Pentoxide; | ||
| SMILES | Phosphorus( 7723-14-0 ) with excess oxygen | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
White, very deliquescent solid wiith irritating odor | |
| MELTING POINT | 580 C (under pressure) | |
| BOILING POINT | sublimes at 300 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 2.39 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Exothermically reacts | |
| pH | < 2 (0.1 N aqueous sol. of phosphoric acid) | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | 4.9 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 3 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 3 Other: water reactive | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| FLASH POINT | Non-combustible | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| Phosphorus Pentoxide is a white, flammable, dangerous, and extremely deliquescent solid; specific gravity 2.39; melting point 580 C (under pressure); sublimes at 300 C. The solid reacts with water violently to produce phosphoric acid. It is prepared by phosphorus reaction with excess oxygen. The crude is then purified by sublimation. Phosphorus pentoxide structure consists of each P atoms linked to three others by oxygen bridges with a terminal oxygen atom. It is used as a strong dehydrating agent, capable even of dehydrating concentrated sulphuric acid into sulphur trioxide. It dehydrates amides to nitriles. End applications include manufacture of phosphorus compounds, purifying sugar, optical glass, heat-insulating glass, medicine, pesticide and surfactant manufacturings. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to yellow crystalline powder | |
| ASSAY |
97.0% min | |
| P2O3 | 0.5% max | |
| IRON | 20ppm max | |
| ARSENIC |
30ppm max | |
| Pb |
10ppm max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 20kgs in Drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 | |
| UN NO. | 1807 | |
| DESCRIPTION OF PHOSPHORUS | ||
|
Phosphorus is a nonmetallic chemical element in group 15 (nitrogen family,
formerly Va) of periodic table; atomic number 15 atomic mass 30.9738; melting
point ca 44.1 C (white); boiling point ca 280 C (white); specific gravity 1.82
(white), 2.34 (red), 2.70 (black); valence -3, +3, or +5 ; electronic config.
2-8-5 or 1s 22s 22p 63s 23p 3. The phosphorus molecule is composed of four
phosphorus atoms, P4. Phosphorus exists in a number of allotropic forms [white
(alpha and beta), red, black and/or violet] in the same physical state. White
phosphorus is a white to yellow waxy substance which ignites spontaneously in
air to form white fumes of phosphorus pentoxide and glows without emitting heat.
Phosphorus is stored underwater as it is extremely poisonous, insoluble in water
(but soluble in carbon disulfide). Commercial production of elemental phosphorus
is prepared from phosphorite or phosphate rock (apatite, an impure calcium
phosphate mineral) reacting with coke and sand or silica pebblesor at high
temperatures in an electric furnace. Calcium silicate is produced as a
by-product. White phosphorus is used as a deoxidizing agent in the preparation
of steel and phosphor bronze. It is also used in rat poisons and to make smoke
screens (by burning) for warfare. When white phosphorus is heated to about 250 C
with air absence, it changes into the red phosphorus. Red phosphorus, a dark
redish powder or crystal, does not ignite spontaneously unless heated to 200 C,
does not phosphoresce and it is a little less dangerous than white phosphorus.
It is used to make matches. Red phosphorus is prepared commercially by heating
calcium phosphate with sand and coke in an electric furnace. Black allotrope is
obtained industrially by heating at 300 C under pressure with a mercury
catalyst. It has a layer structure and is stable. The major use of phosphorus
compounds is in fertilizers, mainly as a mixture called superphosphate (calcium
hydrogen phosphate), obtained from phosphate minerals by sulfuric acid
treatment; and in nitrophosphates. Phosphorus is burned to make phosphorus
pentoxide [phosphorus(V) oxide], a white solid used as a chlorinating agent in
organic chemistry, as a drying agent and mainly converted to phosphoric acid
used to make phosphates for fertilizers, electro chemical polishing and shaping,
electroplating, metal cleaning and pickling in metal treatment by reaction with
water. Phosphorus is highly reactive. A wide range of compounds is formed for
uses in detergents, water softeners, pharmaceuticals, dentifrices, and in many
other important applications. It forms metal phosphides and covalently bonded
phosphorus(III) and phosphorus(V) compounds. Phosphoric acid can combine with
certain alkaline elements to form salts called phosphates.
|
||